Counterfeiting threats are real. Brands in all industry sectors, from apparel to health, beauty and electronics, are grappling with questions on how to ensure that their brand value is not undermined by scammers selling fake copies of their goods in the real market space.
As per a recent report by Authentication Solution Provider’s Association (ASPA), counterfeiting incidents have risen steadily in the last few years, and in 2019, these have increased by 24% as compared to 2018. The highest number of cases have been reported in currency, FMCG, alcohol, pharma, documents, agriculture, infrastructure, automotive, tobacco, lifestyle and apparel sectors. Among these, the FMCG sector is most vulnerable as counterfeit incidents in the sector increased by 63%.
Today counterfeiting has become a global industry, threatening the safety of the public eroding consumer confidence in brands, and destroying their reputation.
History of Barcodes
Problems associated with counterfeiting
Falsified products, especially belonging to healthcare, can have serious adverse effects on the wellbeing of a person. For example, if a person purchases a fake skincare product though the packaging and substance may look similar to the authentic brand but can cause skin infections and rashes when applied.
These consequences, when blown out of proportion using the power of instant communication through social media channels, is likely to damage the brand’s reputation and in turn affect consumer trust and hence sales. Customers are generally unaware that the product they bought is falsified, adds to it.
Secondly, there is also a business hazard of counterfeit goods, as this contributes to a loss of revenue for manufacturers. With the advent of technology and emergence of e-commerce portals, exact product packaging can be duplicated, making it even more difficult to catch counterfeit with the bare eye or on online portals. What’s real and what is fake has become very difficult and the lines become very blurred.
History of Barcodes
Need for an effective product traceability to stop counterfeiting
This is more critical than ever for brands to protect themselves and ensure that their brand values are not compromised by counterfeit products and gain consumers’ trust.
Traceability technology provides a tool to brands owners to keep themselves one step ahead in combating the counterfeiting of products. Brand owners can easily locate the entire batch of their products or any single product from the batch in the supply chain, with an effective traceability system, and can take corrective action whenever needed or required which helps in detecting counterfeiting at any level of the supply chain process.
Traceability refers to the organization’s ability to identify, track and trace elements of a product/consignment as it moves along the supply chain from raw goods to finished products.
To prevent counterfeiting of products, GS1 India offers a global standards based traceability service that enables brand owners to easily track and trace their products right through the journey from origin to the point of sale and consumption. Effective end-to-end traceability service not only helps them to respond to the problems immediately but also anticipate and prevent problems effectively. It helps them to secure data in real-time which further helps to reduce the risk of counterfeiting when products are still in transit.
Learn more – about GS1 Traceability Service.
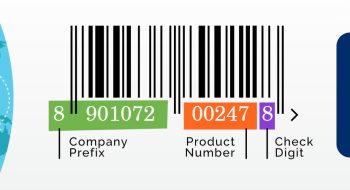
A core component for this is product identification. This can be done by using barcodes/ serialised barcodes on product labels. To know more and register for unique product identification numbers, visit: https://www.gs1india.org/content/register-for-barcodes/
Realising the magnitude of damage caused by counterfeiting to the Indian economy, brands and consumers, Authentication Solutions Providers’s Association (ASPA) and GS1 India have joined hands and signed MOU to take the fight against counterfeiting to the next level in India, using global standards.
To avail the benefits of GS1 India’s Traceability service for a transparent supply chain process.