Introduction
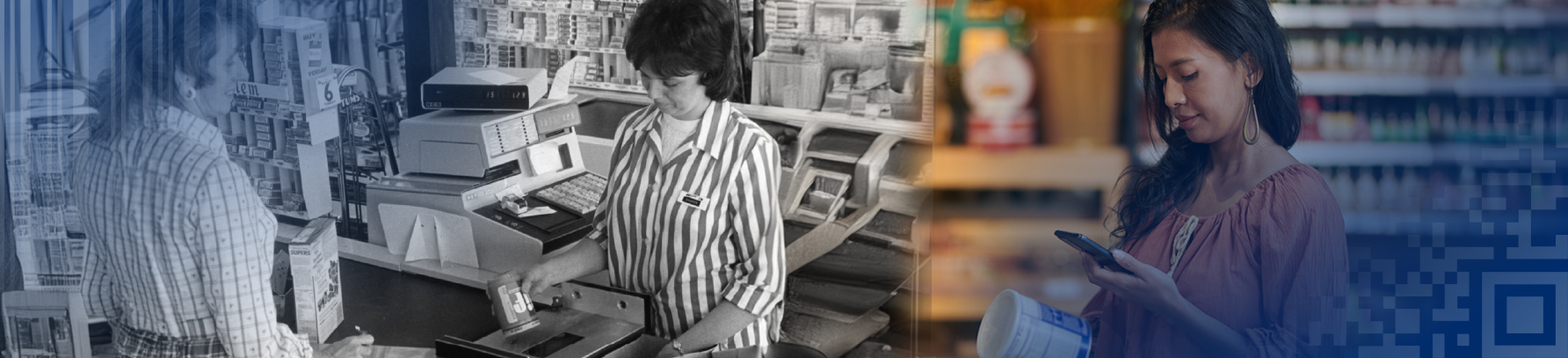
Barcodes are ubiquitous in modern life, appearing on everything from groceries to electronics. These simple yet powerful tools have changed various industries by enabling quick and accurate data capture and tracking. Their importance cannot be overstated, as they play a crucial role in retail, logistics, healthcare, and more, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and convenience. In this blog, we will learn Who Invented the Barcode, its inventors, and a lot more things in product tracking, that barcodes have revolutionized.
Who Invented the Barcode?
The concept of the barcode was first conceived by Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver in the late 1940s. They sought to create a system that could automate the process of checking out in grocery stores. The initial design was a series of concentric circles resembling a bullseye. This design, though innovative, had its limitations, leading to the development of more practical linear barcodes. Their invention paved the way for the modern barcode system that we use today.
Impact of the Barcode on Industries
Barcodes have profoundly impacted various industries, streamlining operations and enhancing productivity. Their role in improving efficiency, accuracy, and overall operational success is undeniable across multiple sectors.
Retail and Commerce
Barcodes have changed the retail industry by significantly improving the speed and accuracy of transactions. Major retailers quickly adopted barcode technology, which allowed for the automation of inventory management, pricing, and sales tracking. The adoption of barcodes has enabled real-time data collection, which facilitates more efficient inventory control, reduces errors, and enhances the customer checkout experience. For instance, retailers like Walmart and Tesco have implemented extensive barcode systems to optimize their operations, leading to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies. The ability to quickly scan and process items has also minimised human errors, ensuring accurate pricing and inventory levels, thereby improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Healthcare
The primary goal of barcoding in healthcare is to enhance patient safety by minimising medication errors and ensuring that the right patient receives the correct medication in the appropriate dose and route. Additionally, barcoding improves inventory management and supply chain operations and facilitates efficient product recalls when necessary.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
The role of barcodes in enhancing supply chain efficiency is unparalleled. Barcodes enable real-time tracking of products from the point of origin to the final destination. Logistics companies leverage barcodes to streamline the sorting and shipping processes, reducing the likelihood of errors and ensuring timely deliveries. Companies like FedEx and UPS rely heavily on barcode technology to track shipments, manage inventory, and improve customer satisfaction. By providing accurate and immediate data, barcodes help logistics firms optimise route planning, reduce delivery times, and manage resources more effectively. This efficiency translates to cost savings and improved service levels for clients and customers.
Food Industry
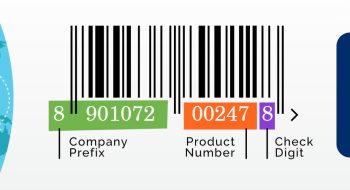
Barcodes have become an important tool in the food industry, streamlining operations from farm to table. They offer a seamless bridge between physical goods and digital information, facilitating efficient identification, tracking, and management of food products. Barcodes store essential data such as product type, origin, and price, which can be easily scanned and processed throughout the supply chain. This capability is critical for ensuring product traceability, maintaining food safety, and complying with regulatory standards. For example, the Universal Product Code (UPC) and the GS1 DataBar are commonly used in the food industry to encode batch numbers, expiration dates, and other vital information, ensuring that food products are properly tracked and managed.
Development and Evolution of Barcode Technology
The journey of barcode technology has been marked by significant milestones and continuous improvements.
The Original Bullseye Barcode
The first barcode design, created by Woodland and Silver, was a circular pattern known as the bullseye barcode. This design aimed to be scanned from any direction, but it faced practical challenges, such as printing inconsistencies and scanning difficulties. Despite its limitations, it laid the groundwork for further innovations.
The Transition to Linear Barcodes
In the 1970s, barcode technology underwent a significant transformation with the development of the Universal Product Code (UPC). George Laurer, an engineer at IBM, played a pivotal role in refining the linear barcode format. His work addressed the limitations of the original design and made it more suitable for commercial use. The linear barcode, or UPC, became the industry standard due to its simplicity and reliability.
The UPC Barcode
The UPC barcode, introduced in 1974, was a game-changer for the retail industry. It allowed for rapid and accurate scanning of products at checkout, significantly speeding up the process and reducing human error. The adoption of the UPC barcode by major retailers and manufacturers marked the beginning of a new era in retail operations. Today, UPC barcodes are an integral part of the global supply chain, used by millions of companies worldwide.
George Laurer’s Contribution
George Laurer’s contribution to the development of the linear barcode cannot be overstated. His work on the UPC barcode design addressed the challenges of the earlier bullseye design and made barcode technology more practical for everyday use. Laurer’s innovations in barcode technology have had a lasting impact on various industries, from retail to healthcare to logistics.
Technological Advancements in Barcode Systems
Barcode technology has continued to evolve, with new innovations enhancing its capabilities and expanding its applications.
From Linear to 2D Barcodes
The transition from traditional linear barcodes to 2D barcodes, such as QR codes, represents a significant advancement in barcode technology. 2D barcodes can store much more information than linear barcodes, including URLs, text, and even multimedia. They are used in various applications, from marketing and advertising to inventory management and authentication. The versatility and increased data capacity of 2D barcodes have made them an essential tool in the digital age.
Conclusion
The invention of the barcode by Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver, and its subsequent refinement by George Laurer, has had a profound impact on modern technology. Barcodes have revolutionised industries by enabling efficient data capture and tracking, reducing errors, and enhancing operational efficiency. The legacy of Woodland, Silver, and Laurer lives on in the widespread use of barcodes today, as they continue to be an indispensable tool in the global supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who Invented the Barcode?
The barcode was invented by Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver in the late 1940s. Their initial design was a circular bullseye pattern, which later evolved into a more practical linear barcode.
2. When was the first barcode invented?
The concept of the barcode was first conceived in 1948 by Woodland and Silver. The first practical implementation of barcode technology, the UPC barcode, was introduced in 1974.
3. Who owns the barcode?
No single entity owns the concept of the barcode. However, GS1 is the global standards organisation that manages and allocates barcode numbers, ensuring their unique identification and standardisation.
4. What is a 6-digit bar code?
A 6-digit barcode typically refers to a truncated version of a longer barcode, often used for specific applications where less information needs to be encoded. However, standard barcodes, such as the UPC, usually have more digits to ensure unique identification.